- The owner is no longer capable of adequately maintaining the elephant's welfare.
- If it's determined that the elephant will receive better care in the new circumstances compared to its current situation.
- The Chief Wildlife Warden may deem it necessary for the elephant's better upkeep based on the specific circumstances of the case.
- Before a transfer within a state, the elephant's health must be confirmed by a veterinarian.
- The suitability of both the current and prospective habitats must be verified by the Deputy Conservator of Forests.
- Approval or rejection of the transfer is at the discretion of the Chief Wildlife Warden based on these assessments.
- Similar conditions apply for transferring elephants outside a state.
- Additionally, theelephant's genetic profile must be registered with the MoEF&CC before the transfer.
- The elephant must be accompanied by a mahout and an elephant assistant.
- A health certificate from a veterinary practitioner confirming fitness for transport is mandatory.
- Transport should occur after the quarantine period, if required for contagious diseases, is completed.
- Proper feeding and watering arrangements must be made during transport.
- Tranquillisers/sedatives shall be used to control nervous or temperamental elephants upon prescription by the veterinary practitioner.
Note
- Until August 2022, the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 explicitly prohibited the trade in wildlife including both wild and captive elephants.
- The Captive Elephant (Transfer or Transport) Rules, 2024 stem from amendments to the Wildlife Protection Act in 2022 exempting captive elephants from the prohibition on wildlife trade.
- A Parliamentary Committee, recommended the deletion of this exemption clause for elephants and providing only an exemption for elephants owned by temple trusts and argued that a “careful balance” between traditions and conservation was needed.
- Despite recommendations to delete this exemption, the final amended act retains it, allowing transfers only for elephants with an existing certificate of ownership.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
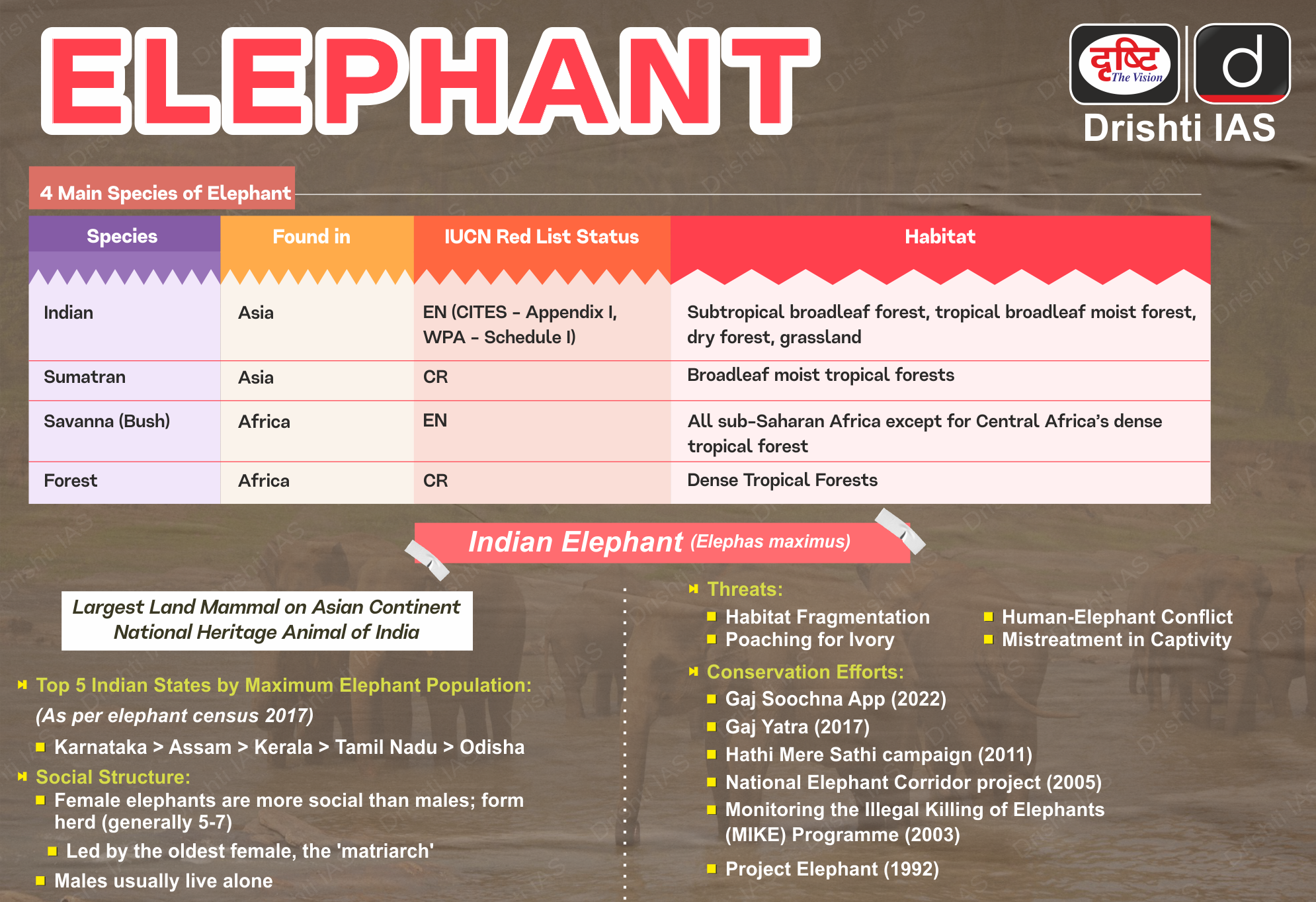
Q. With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female.
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 onlyAns: (a)